Test Methods
Below are the Test Methods employed by Fujipoly.
Test Method of Thermal Conductivity by ISO / CD 22007-2
Fujipoly Test Method: FTM P-1612 (Hot Disk method)
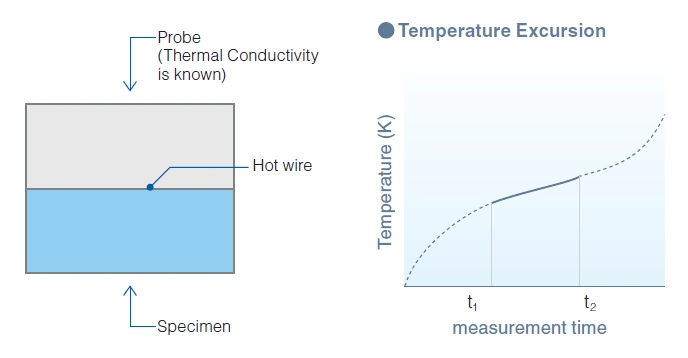
The probe of which the thermal conductivity is known is put on the specimen. Then the hot wire is given constant electric power.
1. Method
The probe of which the thermal conductivity is known is put on the specimen. Then the hot wire is given constant electric power.
2. Principle
A thermal conductivity is given by the equation below.
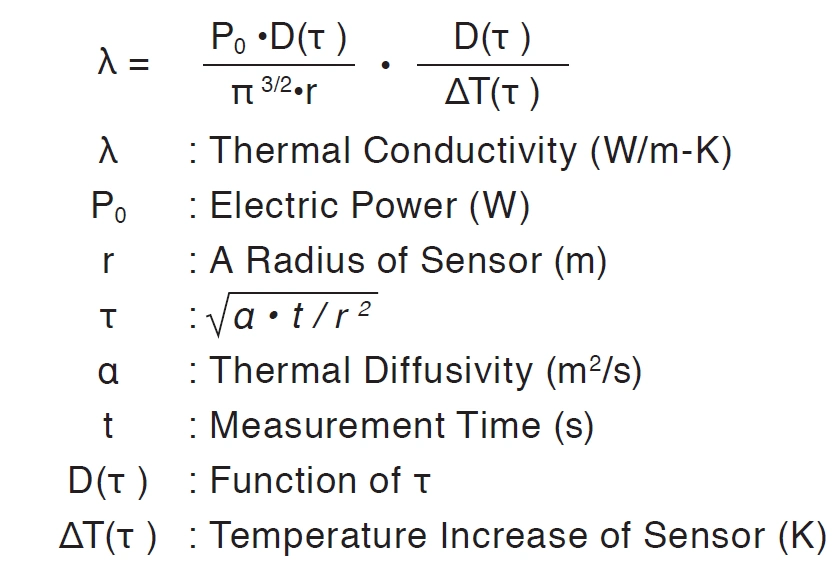
3. Apparatus
| Thermal Conductivity meter | TPA-501 |
| Sensor | RTK Polyimide |
Test Methods of Thermal Conductivity by ASTM D2326 equivalent
Fujipoly Test Method: FTM P-1620 (Hot Wire method)
1. Method
The probe of which the thermal conductivity is known is put on the specimen. Then the hot wire is given constant electric power.
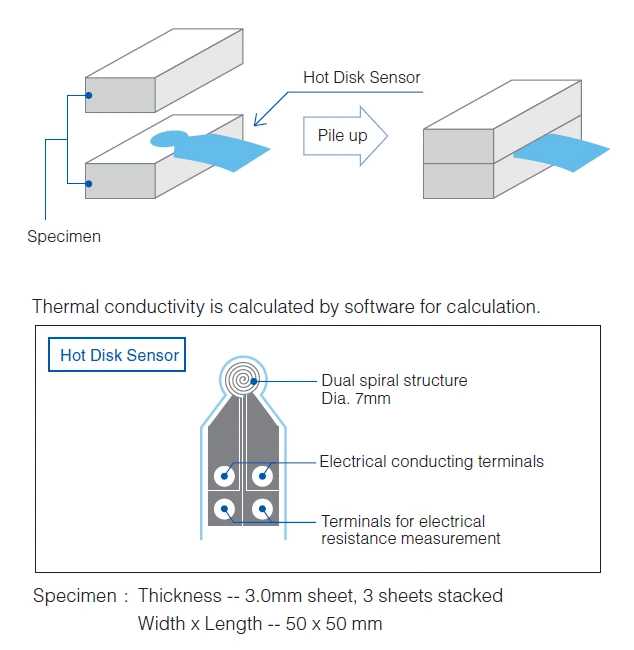
Thermal conductivity is calculated by software for calculation.
| Specimen | Thickness — | 0.1 to 2.0 mm |
| Width x Length — | Min. 120 x 60 mm |
2. Priciple
A thermal conductivity is given by the equation below.
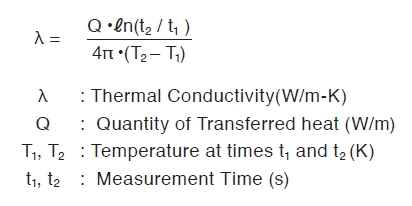
3. Apparatus
| Thermal Conductivity meter | QTM-D3 |
| Calculator | PC9801BX2 |
| Probe; | QTM-PD1 |
Test Methods of Thermal Resistance by ASTM D5470 equivalent
Fujipoly Test Method: FTM P-3050 (TIM Tester method)
1. Principle
Thermal Resistance

2. Measuring Equipment
Analysis Tech TIM Tester 1300s
The Analysis Tech TIM Tester 1300 automatically includes the overall estimated accuracy with the thermal impedance data. This measuring equipment conforms to the test method ASTM D5470, Thermal Transmission Properties of Thermally Conductive Electrical Insulation Materials with the most recent revision.
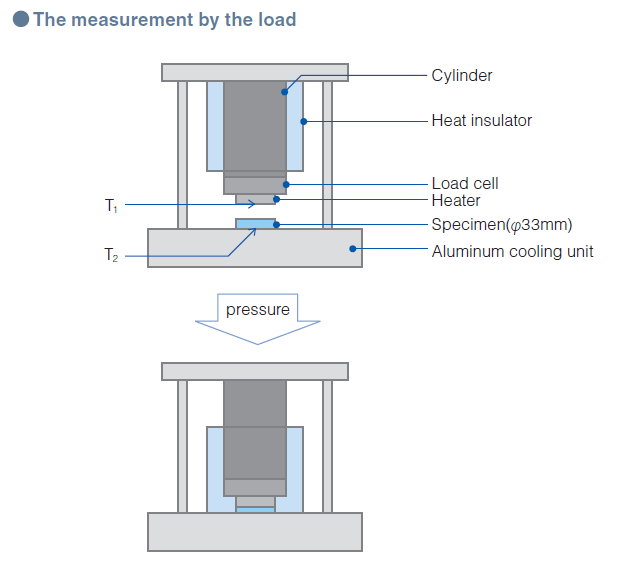
Test Method of Thermal Resistance and Thermal Conductivity by ASTM D5470 modified
Fujipoly Test Method: FTM P-3030 (Guarded Hot Plate method for reference)
1. Principle

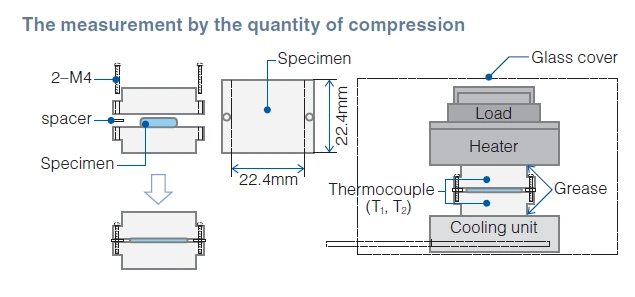

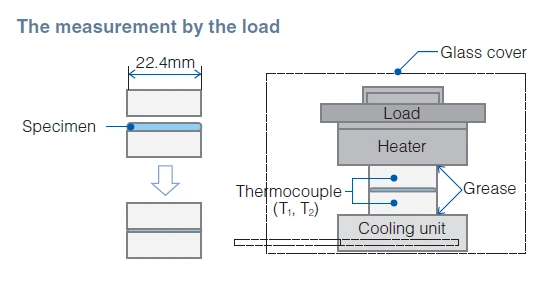
Test Method for Thermal Resistance by Fujipoly Original
Fujipoly test method: FTM P-3010(TO-3 method) which gives ASTM D5470 equivalent value.
1. Test Method
2) 20 Watt power is applied to the transistor.
3) After three minutes, the thermal resistance is calculated based on the following formula (B).
- 1) Punched-out specimen in TO-3 package is located between a transistor and heat sink, and secured with screws the position (A),using a screwdriver.
- 2) 20 Watt power is applied to the transistor.
- 3) After three minutes, the thermal resistance is calculated based on the following formula (B).
2. Principle
Formula for Thermal Resistance calculation.
| (B) | : Rt = ( Tc –Tf ) / P0 |
| Rt | : Thermal resistance K-in2 / W) |
| Tc | : Transistor temperature (K) |
| Tf | : Heat sink temperature (K) |
| P0 | : Heat flow (W) |
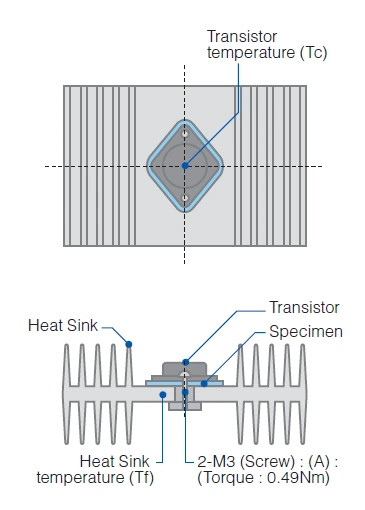
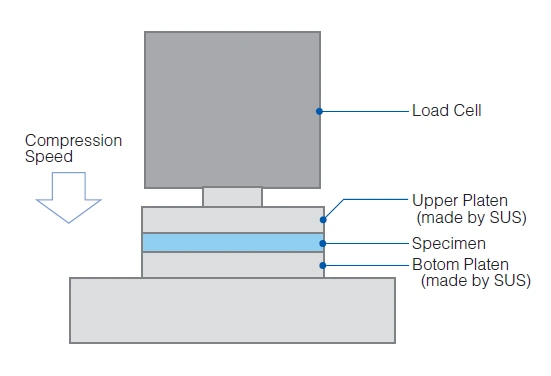
Test Method of Compression Force by ASTM D575-91(2012)
1. Test Method
Compression test in which the force required to cause a specified deflection is determined.
2. Test Condition
| Specimen | Dia.28.6mm (1.13in) Thickness is according to each materials |
| Number of specimens; 3pcs | |
| Platens | Dia.28.6mm (1.13in) |
| Compression Speed | 5.0mm/min (0.2in/min) |
| *Fujipoly original speed |
[Note]
Measuring Form in Place Gap Filler type:
The specimen is pressed till setting a gap, and then waiting for the load to settle down. Setting a gap: 0.5mm or 1.0mm.
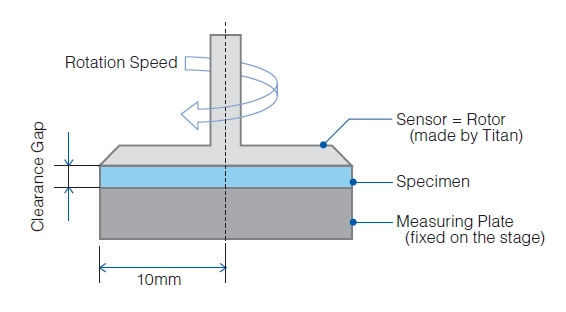
Test Method of Viscosity by ASTM D1824 – 95(2010)
1. Test Method
Covers the measurement of SARCON’s viscosity at low shear rates.
2. Apparatus
| Equipment | HAAKE RotoVisco 1 |
| Sensor | C20/2 |
| Clearance Gap | 0.5mm |
| Rotational Speed | 0.5(1/s), 1.0(1/s) |
Fujipoly has been utilizing TIM Tester method and Hot Disk method since Fujipoly defined them as Fujipoly standard.
Current Fujipoly Standard test method;
• Hot Disk method for Thermal Conductivity testing
• TIM-Tester method for Thermal Resistance testing
Back Ground
• Hot Wire method was inefficient to test over 4 W/m-K material for Thermal Conductivity due to unstable Contact Thermal
Resistance, and it was worse than TO-3 method in 2000.
• Guarded Heater method was more efficient than TO-3 method, so it was defined as Fujipoly standard method in 2002.
• After that, Hot Disk method and TIM-Tester method were both defined as latest Fujipoly standard method due to so reliable in 2012.
1) Hot Disk Method for Thermal Conductivity (TC) measuring
[ Advantage ] The measured TC does not depend on the specimen’s surface-roughness and hardness due to wide measuring range. And it is more stable than How Wire method.
[ Disadvantage ] Specimen’s dimensions, 50 sq-mm x 7mm thickness is so big that the measured TC is a little different from the true one.
2) TIM Tester Method for Thermal Resistance (TR) measuring
[ Advantage ] The measured TR can be close to the true TR due each specimen’s thickness.
[ Disadvantage ] The measured TR depends on the specimen’s surface-roughness or hardness, and it is not stable.
3) Hot Wire method for TC measuring.
[ Problem ] The measured TC is unstable depending on the specimen’s surface-roughness due to fixed-point type thermocouple.
4) Guarded Heater method modified ASTM D 5470 for TR measuring.
[ Problem ] The measured TR is lower than the true one because it is impossible to prevent heat dissipation from the Aluminum blocks which hold the specimen. It is also unstable under continuous compression depending on specimen’s deformation which comes from small difference in hardness and modulus.
